|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Data Characteristics |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Data Characteristics |
  
|
(go directly to our Notes on Meteo)
Beginning date /End date/Legal time
The Data Characteristics section of the form first mentions the period coverage and the time reference system of the .MET file. Note that the latter is always Legal Time, and shall not be confused with the Source file time reference which may be different.
Time Shifts
During the simulation PVSyst has the possibility to apply a time shift correction, expressed in minutes, to the calculation point which is always the middle of the hourly interval. Setting an adequate correction is extremely important to get good calculation results. The time shift defined in the .MET file is the result of an iterative process. The correction is considered as active when the user checks the box "Apply time shift correction" and saves the file. Once again, this correction shall not be confused with the values specified in the source file.
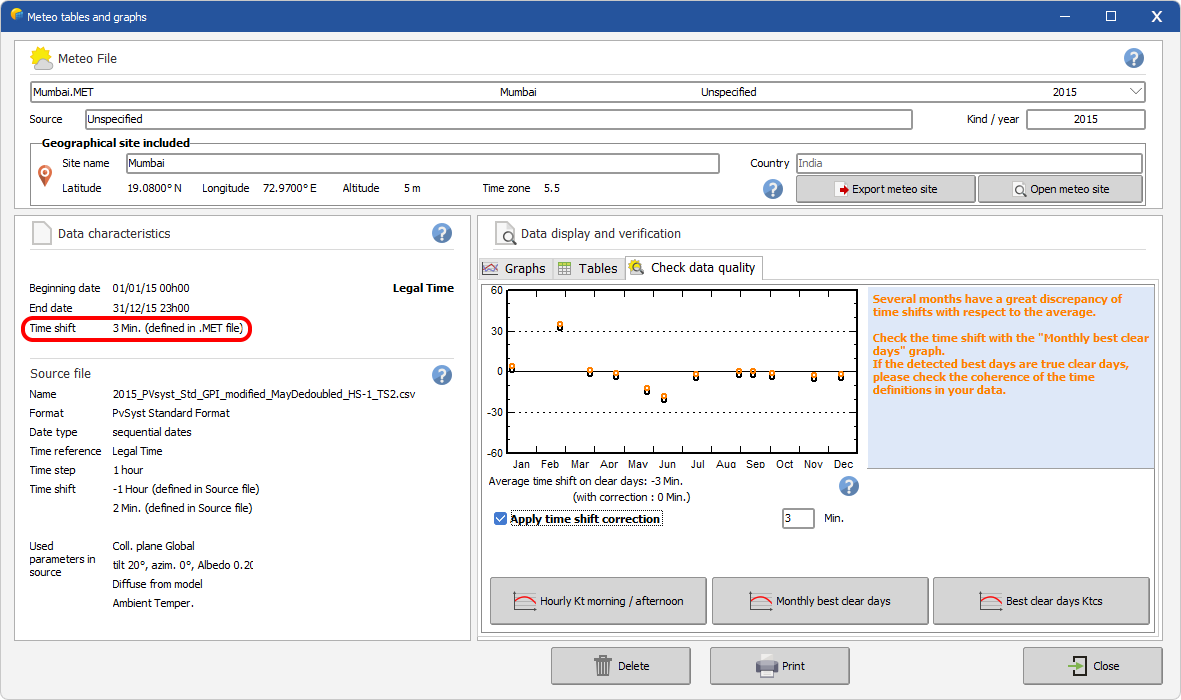
As an example, in the screen shot given below :
- the user has first defined a -1 hour shift together with a + 2 minutes time shift in a PVSyst standard file
- he finally decided to set a +3 minutes time shift after considering the Check data quality tools of PVSyst.
- the +3 minutes time shift is the value written in the .MET file. It will be applied during the simulation.
| |  |
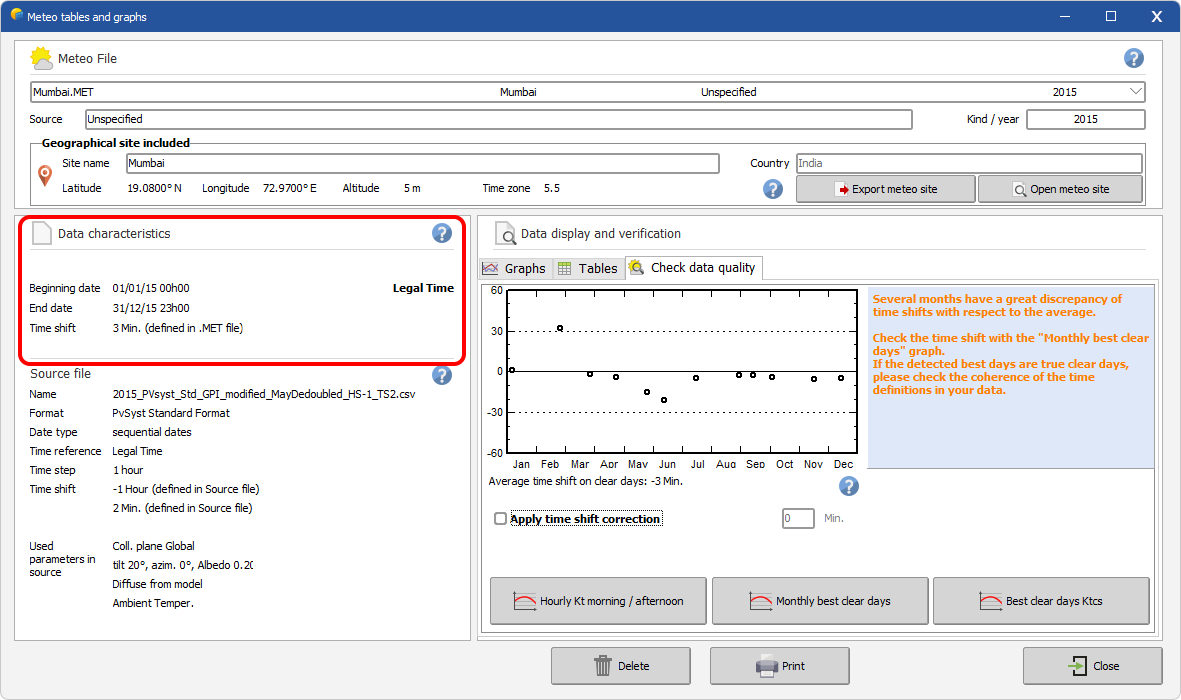
In the screen shot given below, the user decided not to apply the Time Shift defined in the source file. By doing so, PVSyst will not consider any minute shift during the simulation.
Synthetic data
The hourly data may be synthetic, i.e. generated from a stochastic algorithm. Providers such as Meteonorm generate synthetic hourly files. The label Synthetic data covers this specificity, as the year label 1990.
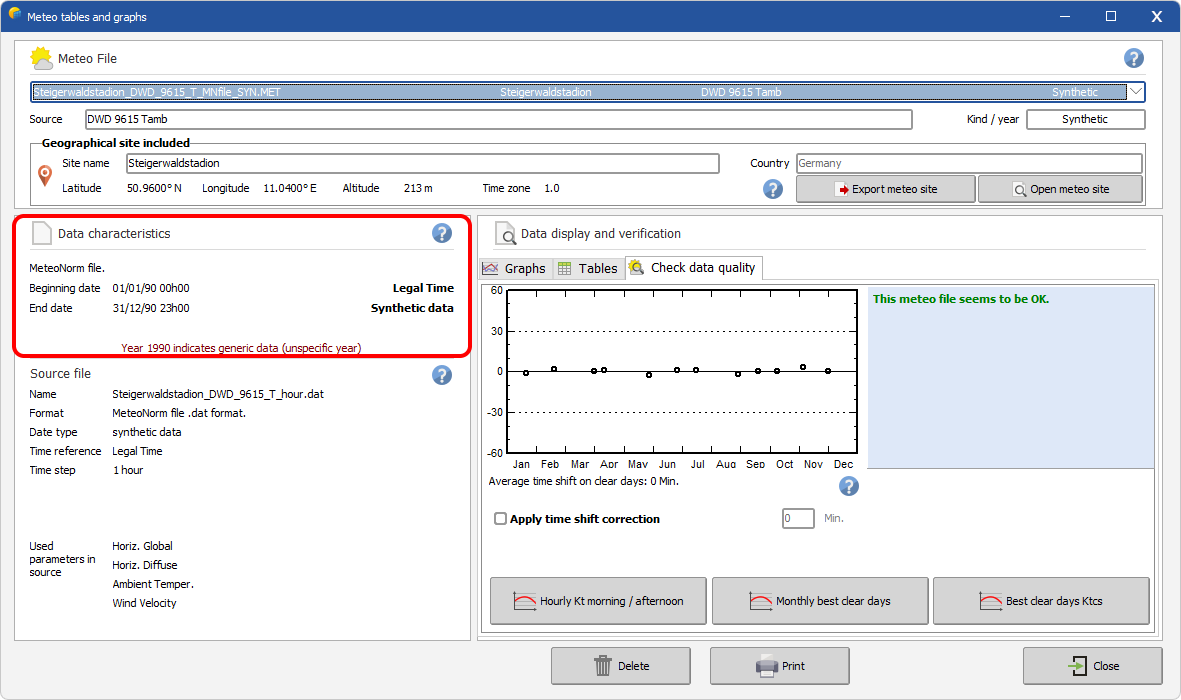
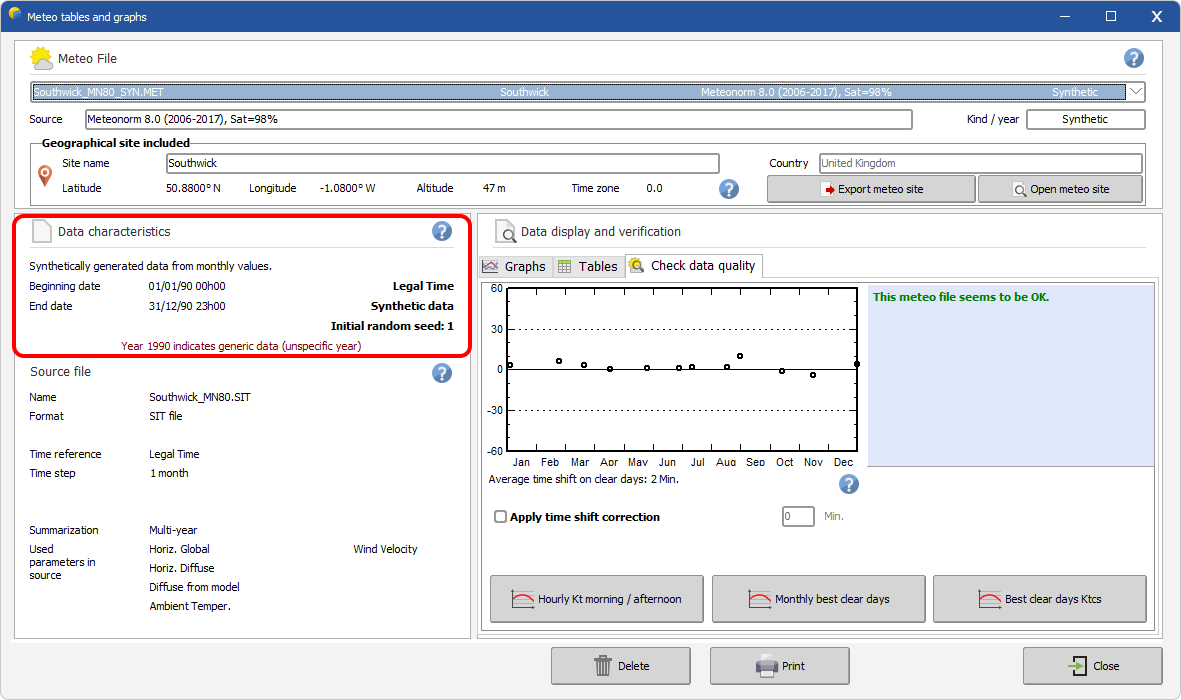
If the synthetic generation has been performed in PVSyst by the MeteonormDLL, then the first random seed is indicated. |
 |
| TMY |
| The label TMY holds for Typical Meteorological Years or Design Reference Years (DRY). As for Synthetic data, the year is stamped 1990. |
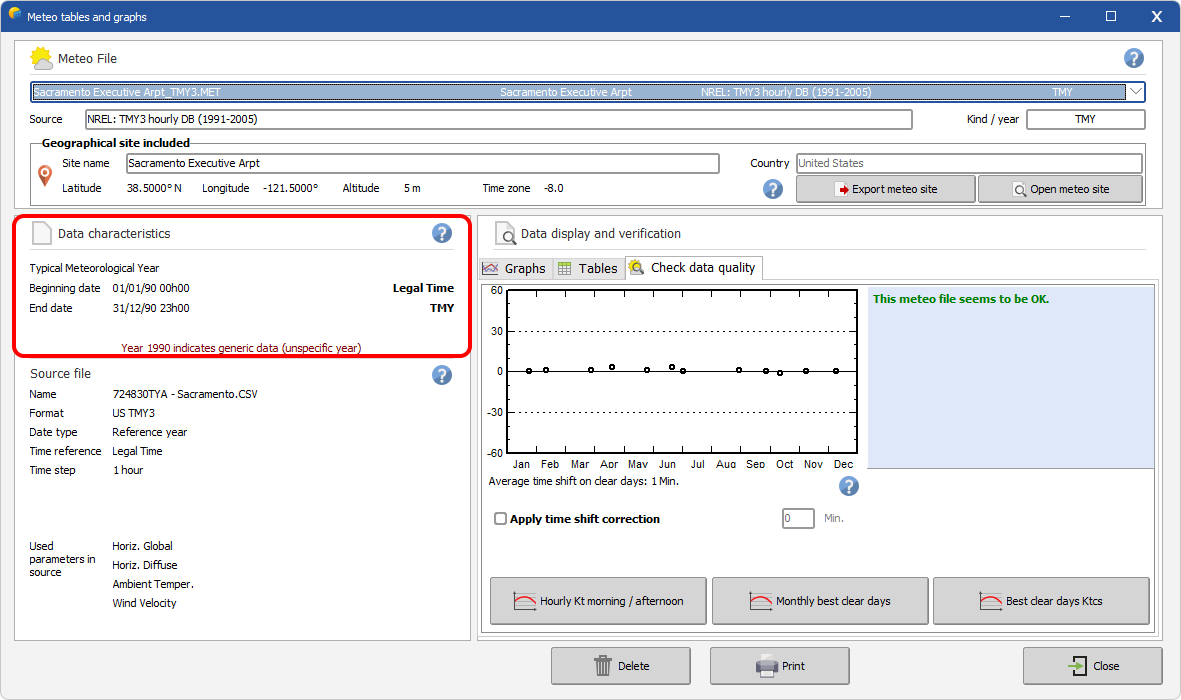 |
Other differences may exist between the MET file data characteristics and the source file data characteristics. For instance,the source file dataset may incorporate discontinuities related to summer time daylight saving shifts, but in the MET file the whole year is consistent with the winter time mode.