Storage: Power's peak shaving
For systems with DC converters on the PV array: see Peak shaving with DC converters.
Principle
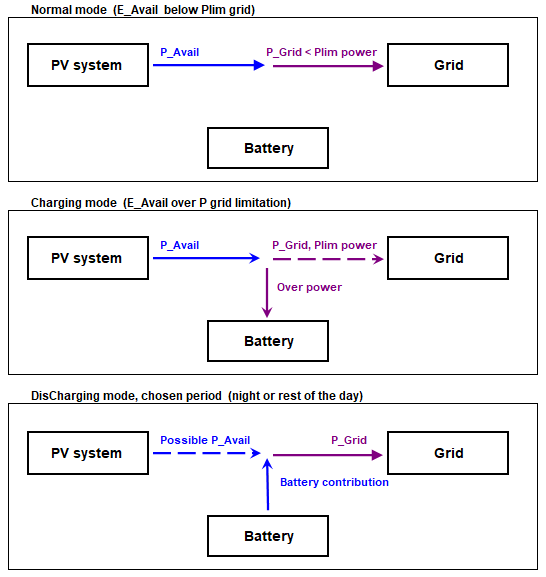
When the injection power is limited by the grid manager, the overload energy could be stored in batteries.
This will have the advantages:
- for the PV plant owner, recovering the energy which would otherwise be lost (at the the price of an additional cost of the stored energy).
- for the grid (large scale): regulate the renewable energy production.
For doing this, we need a battery pack able to store the overpower produced during one day, of higher power than the specified limit.
In practice, if the limit is rather high the storage will only be used episodically, representing a high investment for a low benefit.
For being significant for the grid management, the limit should be rather low, this will require a very big storage system. The price of stored energy (especially due to cycling) becomes crucial for the PV plant profitability.
This mode doesn't involve an internal use of the energy: the energy fluxes are more simple.
Sizing
- Define the Grid Power Limit The maximum PV power at clear sky conditions is displayed in the dialog. Choose a grid power limit below this maximum.
- Specify the Maximum Charger Power Set the charger’s maximum input power by subtracting the grid power limit from the maximum PV power at clear sky conditions.
- Set Battery Inverter Power The battery inverter power can be lower than the charger power, as discharging may extend overnight.
- Determine Battery Capacity Select a battery pack that ideally covers the peak overload energy on a clear day. You may choose a lower capacity for budget considerations. Run simulations to find the optimal size based on financial requirements, accounting for cycling wear costs.
Simulation
The battery will perform daily cycles: it will always be discharged at the end of the night, and will be charged on sunny days when there is excess PV generation.
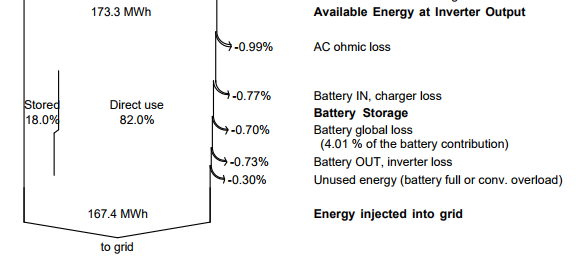
After the simulation, the balances of all these energy fluxes will show up on the loss diagram:
The diagram shows:
- EBatDis: The amount of stored energy, which has an impact on the cycling, i.e. the battery lifetime,
- EBatCh - EBatDis: The battery storage efficiency loss (faradic efficiency, internal resistance, gassing),
- CL_Chrg, CL_InvB: The charger and battery inverter's efficiency losses,
- EUnused: There may be some unused energy, either when the battery is full, or if the charging power overcomes the maximum power of the charger.
- E_Grid: The only use of the electricity in this mode.
We can observe that the only benefit of this configuration is to enhance the system production for the grid when the PV array is highly oversized, at the price of an additional cost of the stored energy.