Grid inverters - Output parameters
Power factor
The grid manager may require to produce some active or reactive energy i.e. define a Power factor.
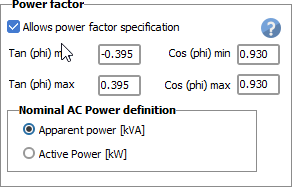
The checkbox Allows power factor specification determines the ability of the inverter to produce reactive energy.
If so, the manufacturer specifies the limits for the phase shift (either as Cos(Phi) lagging and cos(phi) leading, or as Tan Phi limits). The manufacturer also specifies if the PNom value is expressed as an Active power (expressed in kW) or an Apparent power (expressed in kVA).
In the latter case, this limitation corresponds indeed to a limitation on the output current.
NB: in the system, the Power factor is an operating condition, which is set by a specific parameter within the inverter. This is usually fixed for a given period, according to the requirement of the grid manager.
These operating conditions are set in the system parameters (Miscellaneous tools). The values mentioned here are only the limits allowed for this inverter.
Pnom as function of the temperature
The main characteristics of an inverter is the nominal power PNom, i.e. the maximum power which can be delivered to the grid.
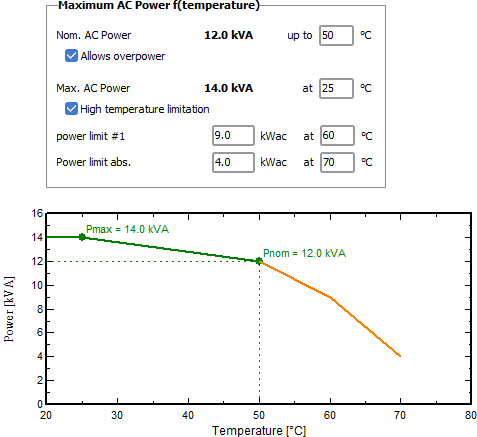
For some inverters the manufacturers specify a maximum power PMax. This is a power which may be attained if the device lies under a given temperature.
For using this enhancement in the simulation, the manufacturer should specify:
- The maximum temperature for attaining PMax
- The temperature at which we will reach PNom.
NB: the option "Allows overpower" will only be active if a PMax value is specified in the main parameters !
Furthermore there may be some limitations when the inverter becomes too hot. Therefore we can specify 2 other temperature levels over PNom, with 2 power levels.
Finally, during the system operation the nominal power may have a temperature profile like this:
Reference temperature
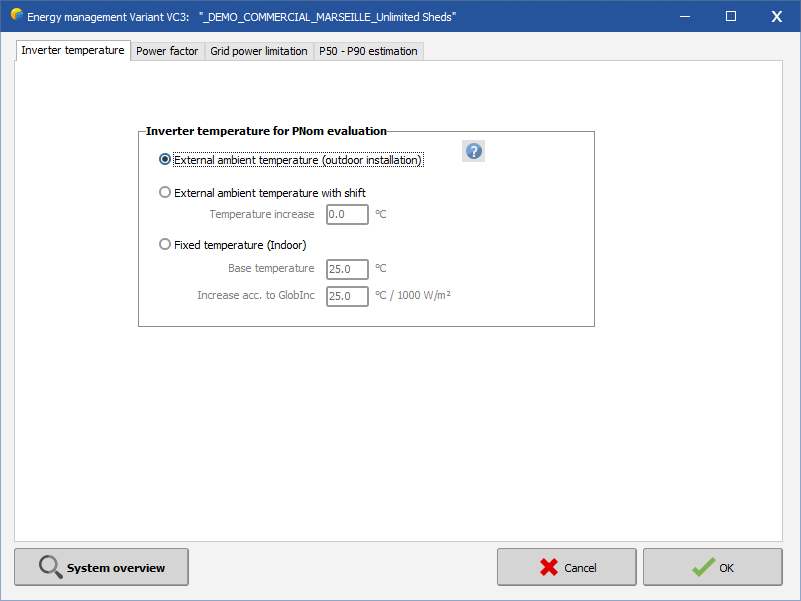
The reference inverter temperature may be specified in the output system parameters (Miscellaneous tools). It can by:
- Ambient external temperature, the usual parameter admitted by manufacturers for outdoor installation.
- Ambient external temperature + specified shift
- Fixed temperature + linear increase proportional to the power (represented by the incident irradiance). This could be used for indoor inverters and not perfect cooling installation.
PNom ratio
The PNom ratio is the ratio of the installed PV power (nominal at STC) with respect to the Pnom(ac) of the inverter. This is indeed a widely-used indicator when sizing the inverter. It is often determined for getting a negligible overload loss.
The value for "No loss" conditions is evaluated during the sizing in PVsyst, and usually lies between 1.25 and 1.30.
However with these modifications of the effective Pnom during operation, these well-accepted values may be very different: when using the PMax increase according to temperature, it may rise by PMax(ac)/Pnom(ac). And defining a power factor will reduce the effective PNom value by cos(phi).